HealthCoach – Heart Health
The heart works as a pump for the movement of blood in the body. There is “de-oxygenated blood” and "oxygenated blood.”

“De-oxygenated blood” is rich in carbon
dioxide and flows from your body towards the heart.
"Oxygenated blood” which is oxygen-rich, after passage through the lungs, enters your heart to flow away from the heart. The human heart along with the lungs, blood vessels and blood itself, are the major parts that make up the circulatory system.Your heart is a muscle and, as with any muscle, exercise is what strengthens it.
Many epidemiological studies have indicated a protective role for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables and fatty acids, (EPA, DHA. ALA), and physical activity against the development and progression of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Source:
“How The Heart Works, the Heart.” NHLBI, NIH, 24 Mar. 2022, www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/heart. Accessed 27 Sept 2022.
Comparison of the Human Heart
A comparison to gorillas when it comes to heart disease show a similarity in the effect of dietary patterns. Gorillas also have a four chambered heart like human beings. Thus, looking at research from a journal article published by Bioscience observing gorilla heart health in captivity, the research revealed that heart disease experienced by gorillas in captivity was attributed to lack of ingesting of their evolutionary plant based diet and move distance daily.
Humans also develop heart disease just like gorillas when they consume industrialized processed foods and do not move distance on a daily bases.
Source:
Cheryl Lyn Dybas, Ilya Raskin, Out of Africa: A Tale of Gorillas, Heart Disease... and a Swamp Plant, BioScience, Volume 57, Issue 5, May 2007, Pages 392–397, https://doi.org/10.1641/B570503. Accessed 27 Sept 2022.


Understanding Heart Health
Per the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Coronary heart disease includes 2 major precursors in obtaining the disease; lack of physical activity and malnutrition (improper nutrition).
Obesity is a complex disease that affects whole body metabolism and is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and Type 2 diabetes (T2D). Physical exercise results in numerous health benefits and is an important tool to combat obesity and its co-morbidities, including cardiovascular disease.
Exercise prevents both the onset and development of cardiovascular disease and is an important therapeutic tool to improve outcomes for patients with cardiovascular disease.
Source:
“In Brief: Your Guide to Healthy Heart.” NHLBI, NIH Publication No.06-5715. 24 Mar. 2022, www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/heart. Accessed 27 Sept 2022
Poor/Lack of Physical activity and effects on Heart
Physical inactivity increases the conditions for obesity. Obesity is an increase excess of unhealthy fatsabsorbed by fat cells in the body causing inflammation. Overtime,the tissue swelling caused by this process affects how your blood vessels carry blood throughout your body and to your heart. The continualbuildupof this occurrence causes plaque.
This makes the heart organ pump harder than natural working overtime.
Source:
“In Brief: Your Guide to Healthy Heart.” NHLBI, NIH Publication No.06-5715. 24 Mar. 2022, www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/heart. Accessed 27 Sept 2022.


Why are there populations without heart conditions? (Tsimane – evidence of no heart disease)
In observing age and heart health, looking at a case study using the Tsimane population in Bolivia, who are in the blue zone(s), health research was conducted on the Tsimane population between 07/02/2014-09/10/2015 and targeted 705 Tsimane. Scores higher than 100 fell in the spectrum for atherosclerotic disease .
To clarify, Atherosclerosis is the solidifying of the arteries due to accumulation of plaque in the inner lining of an artery.Of the 705 Tsimane population sample, those who were older than 75 years of age, 65% had a score of O for their Coronary Artery Calcium score meaning a lower prevalence for heart disease
Tsimané eat around 152 different types of foods, which are all grown in small gardens, and foraged. They supplement their diet with some wild game, like peccary and coatimundi, or fish. In total, their diet breaks down to 64 percent complex carbohydrates, 21 percent proteins, and 15 percent fats.
Source:
The Lancet. "Indigenous South American group has healthiest arteries of all populations yet studied, providing clues to healthy lifestyle." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 17 March 2017.
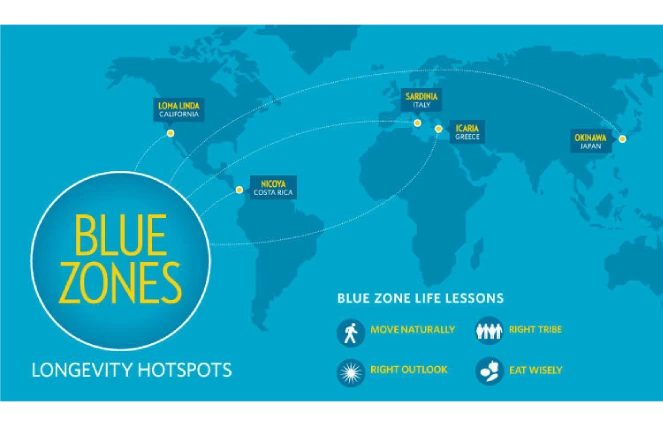
Blue Zones And Longevity
Per research from the National Library of Medicine, Blue Zones are areas where populations reach 100 years of age achieving longevity due to a healthy lifestyle centered on physical activity and healthy nutrition. Referencing another population like the Tsimane, the Nicoyans as an example of a Blue Zone model, who ingest almost no processed food sources and ingest antioxidant-heavy tropical fruits, and calcium and magnesium-rich water in diet patterns.
When it comes to longevity for the Nicoyans, observations interpreted that Nicoyans are more than twice as likely than Americans to reach at least 90 years of age . Another example of a Blue Zone model is the population in Sardinia, Italy. Sardinia has a culture of walking a measure of 5 mountainous miles a day for physical activity allowing them to hold the status of having the world’s longest-age males .
The Danish Twin Study1 established that only about 20% of how long the average person lives is dictated by our genes, whereas the other 80% is dictated by our lifestyle.
The keys are to move naturally daily, have purpose in life, shred stress, 80% Rule. Hara hachi bu—the Okinawan 2500-year old Confucian mantra said before meals reminds them to stop eating when their stomachs are 80% full, plant slant. Beans, including fava, black, soy, and lentils, are the cornerstone of most centenarian diets. Meat—is eaten on average only 5 times per month with small serving sizes, and belong to the Right tribe. The world’s longest lived people chose—or were born into—social circles that supported healthy behaviors, which can be reproduced in any country and or community.
Source:
Buettner D, Skemp S. Blue Zones: Lessons From the World's Longest Lived. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2016 Jul 7;10(5):318-321. doi: 10.1177/1559827616637066. PMID: 30202288; PMCID: PMC6125071.
Effects of exercise, gut health, Omega 3 and Omega 6 diet pattern.
In addition, the increase of omega 3 fatty acids and decrease of omega 6 fatty acids also play a role in managing heart health because omega 3 foods are anti-inflammatory and omega 6 foods then to cause inflammation. Research from a PubMed.gov published study looking at gut microbiome and exercise revealed differences in the ability of athletes and non athletes for anti-inflammatory healing of the body and health promoting bacteria.
The study observed fecal microbial profiles analyzed from 207 athlete and non athletes 11 . By using this analysis, the bacterial make-up of athletes were enriched in diversity of the gut microbiome and those of non-athletes had less health boosting bacteria.
Source:
Simopoulos AP. The omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio, genetic variation, and cardiovascular disease. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2008;17 Suppl 1:131-4. PMID: 18296320. Accessed 2022 Sept 28.
Tarracchini C, Fontana F, Lugli GA, Mancabelli L, Alessandri G, Turroni F, Ventura M, Milani C. Investigation of the Ecological Link between Recurrent Microbial Human Gut Communities and Physical Activity. Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0042022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00420-22. Epub 2022 Apr 4. PMID: 35377222; PMCID: PMC9045144. Accessed 2022 Sept 10.

Deconditioning and its dangers
Every person even with disabilities, require reoccurring exercise to function properly or face the consequence of de conditioning. The research has reported that lack of exercise can lead to loss of body functioning as multiple systems require operation from movement .
Decondition per research conducted on the effects of the “use it or lose it” principle, can be defined as disrupting normal biological functioning due to inactivity or sedentary behavior, obesity, and the effects of aging .
Humans evolved to cover great distances daily to hunt and gather foods, they used their bodies vigorously walking, sprinting, running, throwing, holding, climbing, carrying, pulling, pushing and squeezing.
Source:
Hart DA. Learning From Human Responses to Deconditioning Environments: Improved Understanding of the "Use It or Lose It" Principle. Front Sports Act Living. 2021 Dec 3;3:685845. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2021.685845. PMID: 34927066; PMCID: PMC8677937.